Ozone Manager High Availability
Ozone has two metadata-manager nodes (Ozone Manager for key space management and Storage Container Manager for block space management) and multiple storage nodes (Datanode). Data is replicated between Datanodes with the help of RAFT consensus algorithm.
To avoid any single point of failure the metadata-manager nodes also should have a HA setup.
Both Ozone Manager and Storage Container Manager supports HA. In this mode the internal state is replicated via RAFT (with Apache Ratis)
This document explains the HA setup of Ozone Manager (OM) HA, please check the SCM HA documentation for SCM HA. While they can be setup for HA independently, a reliable, full HA setup requires enabling HA for both services.
Ozone Manager HA
A single Ozone Manager uses RocksDB to persist metadata (volumes, buckets, keys) locally. HA version of Ozone Manager does exactly the same but all the data is replicated with the help of the RAFT consensus algorithm to follower Ozone Manager instances.
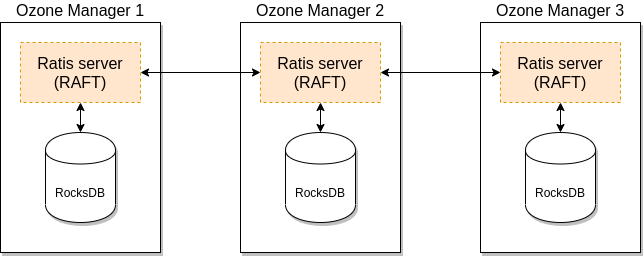
Client connects to the Leader Ozone Manager which process the request and schedule the replication with RAFT. When the request is replicated to all the followers the leader can return with the response.
Implementation details
Raft can guarantee the replication of any request if the request is persisted to the RAFT log on the majority of the nodes. To achieve high throughput with Ozone Manager, it returns with the response even if the request is persisted only to the RAFT logs.
RocksDB instance are updated by a background thread with batching transactions (so called "double buffer" as when one of the buffers is used to commit the data the other one collects all the new requests for the next commit.) To make all data available for the next request even if the background process has not yet written them, the key data is cached in the memory.
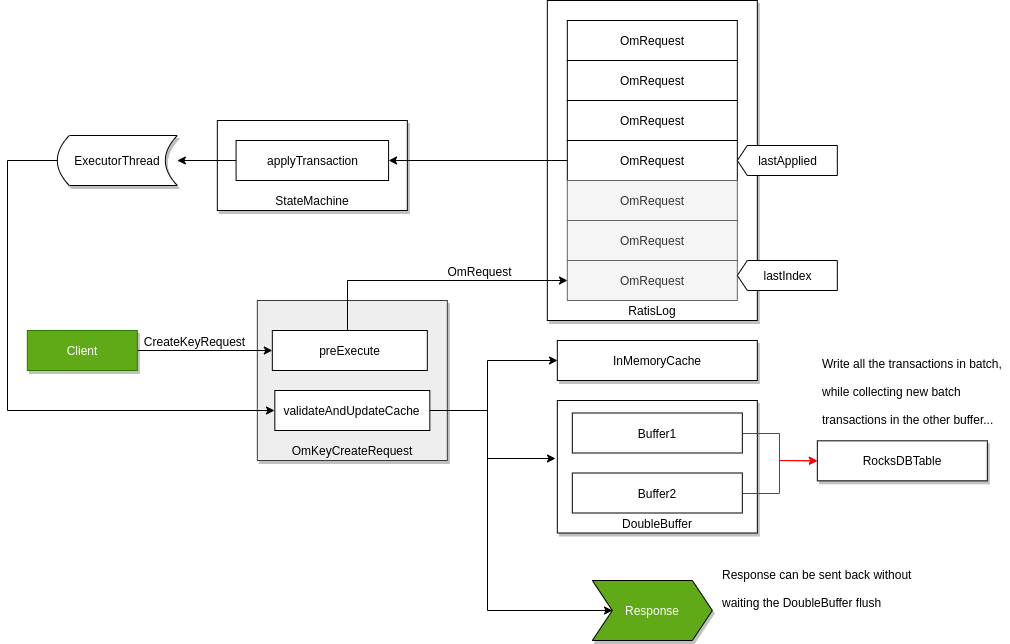
The details of this approach are discussed in a separate design doc but it's an integral part of the OM HA design.
Automatic Snapshot Installation for Stale Ozone Managers
Sometimes an OM follower node may be offline or fall far behind the OM leader's raft log. Then, it cannot easily catch up by replaying individual log entries. The OM HA implementation includes an automatic snapshot installation and recovery process for such cases.
How it works:
- Leader determines that the follower is too far behind.
- Leader notifies the follower to install a snapshot.
- The follower downloads and installs the latest snapshot from the leader.
- After installing the snapshot, the follower OM resumes normal operation and log replication from the new state.
This logic is implemented in the OzoneManagerStateMachine.notifyInstallSnapshotFromLeader();
see the code
in Release 2.0.0.
Note that this Raft Snapshot, used for OM HA state synchronization, is distinct from Ozone Snapshot, which is used for data backup and recovery purposes.
In most scenarios, stale OMs will recover automatically, even if they have missed a large number of operations.
Manual intervention (such as running ozone om --bootstrap) is only required when adding a new OM node to the cluster.
Important Note on Ozone Manager (OM) Disk Space for Snapshots
When an Ozone Manager (OM) acts as a follower in an HA setup, it downloads snapshot tarballs from the leader to its local metadata directory. Therefore, always ensure your OM disks have at least 2x the current OM database size to accommodate the existing data and incoming snapshots, preventing disk space issues and maintaining cluster stability.
References
- Design doc HDDS-505 Ozone Manager HA
- For troubleshooting OM HA snapshot installation issues, see the troubleshooting documentation.
- Ozone distribution contains an example OM HA configuration, under the
compose/ozone-om-hadirectory which can be tested with the help of Docker Compose. - Apache Ratis State Machine API documentation